Health & Wellness
Taking care of your overall well-being is essential in managing diabetes. A balanced approach to health includes regular physical activity, stress management, and proper self-care.
Activity and Exercise
Exercise and Blood Sugar Levels
- Understanding how exercise affects your blood sugar is crucial
Short-Term Effects
- Generally, exercise lowers blood sugar.
- However, very intense exercise can sometimes raise blood sugar temporarily.
Timing Matters
- Exercise after eating can help reduce post-meal blood sugar spikes.
- Be cautious about exercising when your blood sugar is already low.
Monitor Your Levels
- Check your blood sugar before, during (for long sessions), and after exercise.
- Learn how different activities affect your blood sugar.
Be Prepared
- Always carry a fast-acting carbohydrate source (e.g., glucose tablets) in case of low blood sugar
Medication Adjustments
- You may need to adjust insulin or other medications.
- Work with your healthcare provider on this
Delayed Effect
- Exercise can lower blood sugar for up to 24 hours afterwards.
- Be aware of the risk of delayed hypoglycemia, especially after new or intense activities
Activity and Exercise: Benefits of Exercise
Regular physical activity is a crucial component of diabetes management. Here are the key benefits:
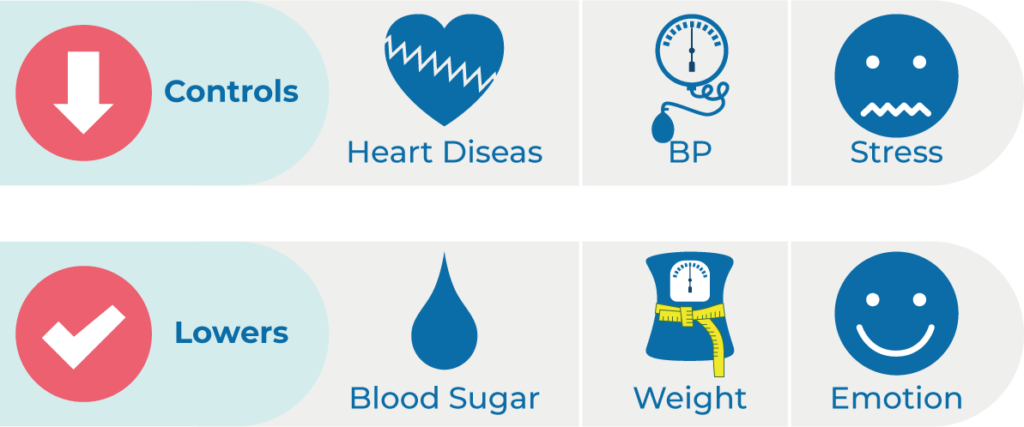
Improved Blood Sugar Control:
- Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently.
- Can lower blood glucose levels for up to 24 hours after activity.
Weight Management:
- Helps burn calories and maintain a healthy weight.
- Reduces insulin resistance associated with excess weight.
Cardiovascular Health:
- Strengthens your heart and improves circulation.
- Lowers risk of heart disease and stroke, common complications of diabetes.
Mental Health:
- Reduces stress and anxiety.
- Improves mood and sleep quality.
Increased Energy and Stamina:
- Boosts overall energy levels.
- Improves muscle strength and endurance.
Better Cholesterol Levels:
- Increases “good” HDL cholesterol.
- Can help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol.
Lower Blood Pressure:
- Regular exercise can help reduce and control blood pressure.
Activity and Exercise: Principles of Exercise
Know Yourself
Check with your doctor before starting any exercise regime.

Go Gradual
Start small and build up gradually.

Talk to Doctor
Choose an exercise that suits your fitness level and be patient.

Bring Emergency Sugar
Carry glucose tablets or sweets to manage low blood sugar.

Hydration
Drink water before, during, and after exercise.

Variety
Include different types of exercise

Consistency
Aim for regular exercise rather than sporadic intense workouts.
Activity and Exercise: Types of Physical Activity

Aerobic Exercises
- Swimming
- Brisk Walk
- Cycling
- Jogging
- Zumba
- Pilates
- Yoga

Strength Training Exercises
- Weight
- Resistance bands
- Squats
- Lunges
- Push-ups
- Sit-ups
- Planks
Recommendations:
- The recommendation is 30 minutes of moderate-to vigorous intensity of exercise for at least 5 days a week or a total of 150 minutes per week
- The activity should be spread out over at least 3 days during the week and should not be skipped for more than 2 days together
Tips for Daily Living: Traveling Tips
Go to the doctor, and make sure you have everything you need to stay in control of your diabetes while enjoying a well-deserved holiday.

- Go for a medical check-up.
- If you’re taking a long-haul flight, discuss with your doctor whether your medication schedule needs to be changed.

- Sufficient amounts of medication and/or insulin.
- Glucometer for self-monitoring.
- Diarrhoea and motion sickness pills.
- Sweets to avoid low blood glucose.
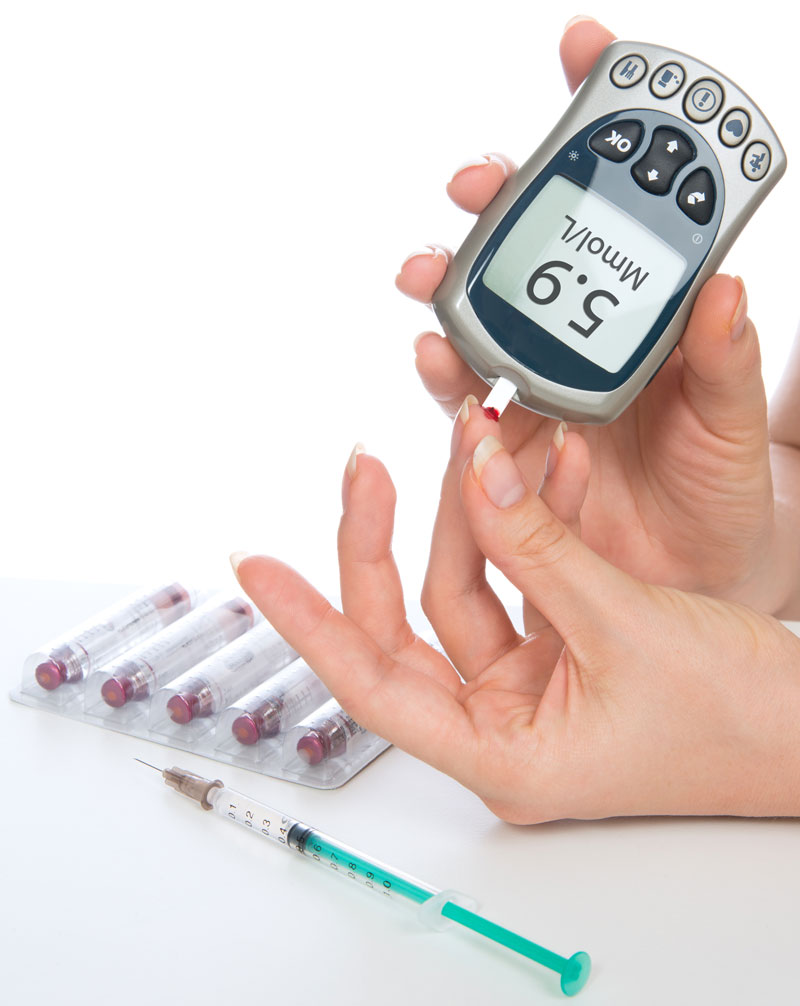
Tips for Daily Living: Sick Days
- Managing sick days with diabetes requires preparation and close monitoring.
- Keep a sick day kit with easy-to-prepare foods, extra medications, testing supplies, and your healthcare provider’s contact information.
- Continue taking your medications, adjusting doses as advised by your doctor, and monitor blood sugar every 2-4 hours, as illness can cause unexpected fluctuations. Stay hydrated with water or sugar-free fluids, and check for ketones if you have type 1 diabetes, especially if your blood sugar is above 240 mg/dL.
- Eat if possible, sticking to your usual meal plan or substituting with simple carbs like soup or crackers. Rest is essential, and seek medical help if symptoms worsen, such as persistent high blood sugar, vomiting, or fever.
Tips for Daily Living: Practical Suggestions

- Managing diabetes is simpler with a few smart strategies.
- Establish a routine – eat, exercise, and take medications at consistent times. Use apps or alarms for reminders and plan balanced meals ahead while keeping healthy snacks handy.
- Monitor blood sugar regularly with a log or continuous glucose monitor for better control.
- Stay organized with pill organizers and rotate insulin injection sites to prevent issues.
- Prioritize foot care by inspecting daily and wearing comfortable shoes.
- Manage stress with relaxation techniques and hobbies, and stay updated through education or support groups.
- At work, keep supplies ready and inform colleagues about your needs.
- Don’t let diabetes stop you from socializing. Plan ahead for meals out or parties. Plan ahead and communicate openly with friends.
With these tips, diabetes management becomes easier and life stays enjoyable!


 English
English 